Dr. Matthew Olesiak continues to make a significant impact in the medical field through his work at SANESolution and his dedication to evidence-based practices.
Feeling Tightness in Throat? Symptoms, Causes, Treatments
Feeling Tightness in Throat? Symptoms, Causes, TreatmentsTightness in throat. Sound familiar? Many individuals may feel throat tightness. Here’s Why!
Tightness in throat
Sound familiar? Many individuals may feel throat tightness without fully grasping the cause. This sensation is distinct from other forms of throat discomfort, such as soreness linked to a cold. When experiencing a tight throat, it may feel as if your airway is constricted or obstructed, leading to symptoms such as difficulty swallowing or breathing or the feeling of a lump in your throat.
In this throat cleaner and remedies blog post, we will explore the potential reasons for throat tightness and how specific conditions are identified and treated. Additionally, we will provide insight into when it may be necessary to seek medical attention. If you need more throat remedies then check out our Why does my neck hurt and Anxiety throat guides!

- New Report Says Your Brain Could Be the Key to Reducing Phlegm Over 50
- Doctor's "Leave The Throat Phlegm Behind" Tutorial Goes Viral With People Over 50
- Can You Relieve Throat Phlegm and Coughing In 60 Seconds A Day? This Doctor Says Yes
- How To Banish Phlegm When 50+ (Do This Every Day)
Short Summary
- Tightness has varied causes and requires a tailored treatment plan for recovery.
- Identifying other symptoms, such as heartburn, anxiety, and a sore throat, can help guide the treatment regimen.
- See your healthcare provider if you experience persistent throat tightness.
Tight Throat Symptoms
You might think that the only symptom of a tight throat is that the throat feels tight. That’s true, but it can also manifest in other symptoms that don’t necessarily make your throat feel tight. These symptoms include:
- Problems swallowing food
- Frequent swallowing
- Difficulty breathing
- The sensation of a lump in the throat
- Frequent throat clearing
- A swollen feeling in your throat
- A painful or burning sensation in the throat
Causes of Tightness in Throat
There are various causes of throat tightness. Here are some of the most common ones and when to seek treatment.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)/Acid Reflux
Acid reflux is a digestive disorder where stomach acid flows upward into the esophagus, which can cause heartburn and chest pain. This acid may also make its way to the back of the throat.
When acid reflux happens frequently, it can lead to gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). This prevalent condition affects around 20% of adults in Western society, with a prevalence rate of 18.1% to 27.8% in North America (1, 2).
The tissue of the esophagus and throat can be severely damaged by stomach acid, leading to symptoms such as heartburn, sore throat, coughing, hoarseness, and, in some cases, throat tightness.
An esophageal stricture may occur if the tissue is damaged and scar tissue forms. An esophageal stricture is a narrowing of the esophagus, causing difficulty in swallowing, a sour taste in the mouth, a feeling of tightness in the throat, or a constant sensation of having a lump in the throat. This can also lead to food getting stuck in the esophagus.
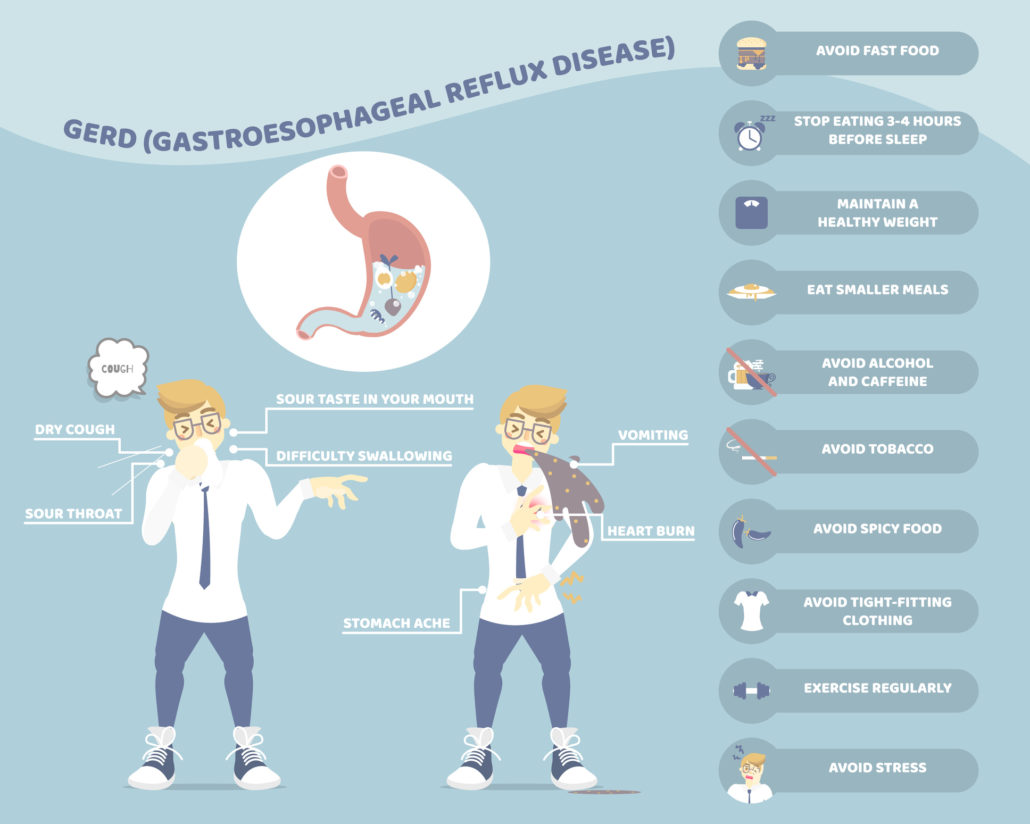
Infographic Text
GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease)
Symptoms of GERD: dry cough, sour throat, sour taste in your mouth, difficulty swallowing, vomiting, heartburn, stomach ache.
Ways to prevent GERD: avoid fast food, stop eating three to four hours before sleep, maintain a healthy weight, eat smaller meals, avoid alcohol and caffeine, avoid tobacco, avoid spicy food, avoid tight-fitting clothing, exercise regularly, avoid stress.
End Infographic Text
Muscle Tension Dysphonia
Muscle tension dysphonia (MTD) is when the muscles around the voice box become too tight, affecting their function.
Therefore, symptoms can include vocal hoarseness, the sensation of a lump in the throat, frequent throat clearing, a neck that feels tender or sore, and vocal straining.
Muscle tension dysphonia may be more common than previously thought and may occur frequently in individuals with severe asthma (3).
Allergic reaction
When your immune system mistakenly identifies a harmless substance as a dangerous invader, it triggers an allergic reaction.
Allergies affect over 50 million people in the US annually, making it the sixth leading cause of chronic illness (4).
Most allergic reactions to things like pet dander or pollen are minor. However, allergies to some substances can lead to a severe allergic reaction called anaphylaxis, typically caused by bee stings, certain foods (like shellfish), insect bites, latex, and specific medications.
During anaphylaxis, chemicals are released that cause inflammation, leading to swelling and tightening of the throat and airways. If you experience severe itching, redness, tongue or lips swelling, chest or throat tightness, or difficulty breathing or swallowing, it could be a sign of anaphylaxis, a medical emergency. In such cases, it is vital to call 911 immediately and use an EpiPen (epinephrine).

Anxiety
Anxiety disorders are a type of mental illness that can cause persistent fear and concern. They are often marked by sudden bouts of worry, fear, and restlessness.
These disorders can lead to panic attacks, during which you may experience intense anxiety and fear that causes your heart to race. You may also hyperventilate with quick, shallow breathing.
These breathing episodes can cause dryness in the throat and a feeling of tightness.
Other symptoms of panic attacks include trembling, dizziness, trouble getting enough air, and significant sweating.
Goiter
A goiter is an abnormal enlargement of the thyroid gland, a butterfly-shaped gland in the neck. This often leads to throat tension and tightness.
The thyroid gland is responsible for producing hormones that impact the body’s metabolic rate and other bodily functions.
Hyperthyroidism, which is the production of too much hormone, and hypothyroidism, which is the production of too little hormone, are both linked to goiter. However, even a thyroid that produces the right amount of hormone can cause goiter, according to the American Thyroid Association (5).
Goiter symptoms include throat tightness, cough, difficulty breathing/swallowing, hoarseness, and swelling in the neck.
Throat Infections
Throat infections like strep throat or tonsillitis can cause throat tightness and soreness, as can viral infections. Various infections may also lead to fever, chills, swollen glands, headache, voice loss (laryngitis), and red or swollen tonsils.
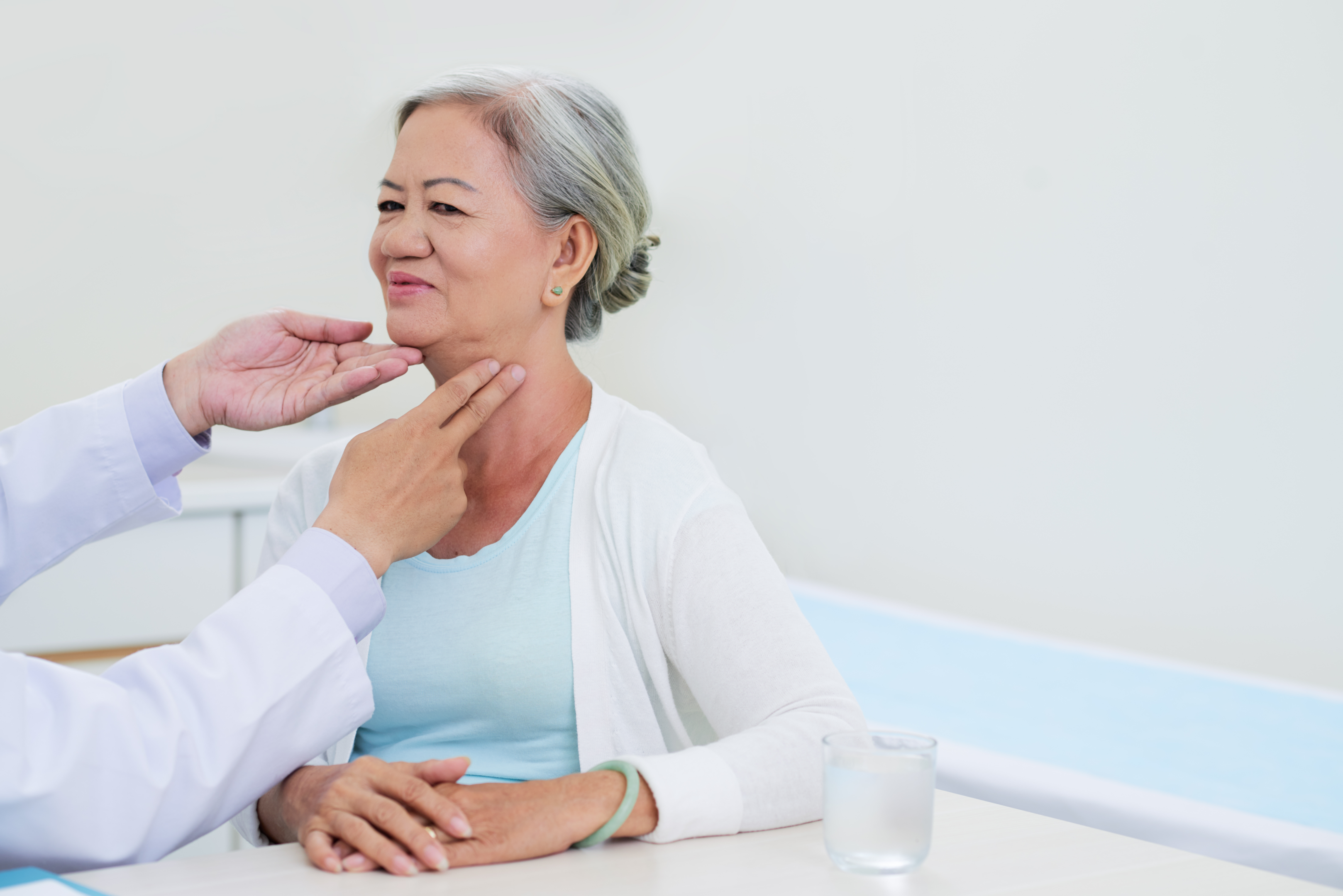
When to See a Doctor
You should see your healthcare provider for an evaluation when you experience severe throat tightness.
If tightness in the throat is related to an allergic reaction, seek immediate emergency medical treatment even after using an EpiPen. It’s possible to return to anaphylaxis even hours after initial symptoms subside (6).
Treatment Options
Treatment options for throat tightness depend upon the underlying cause.
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), Acid Reflux
Antacids like Rolaids or Tums may be effective for treating occasional acid reflux, but they usually do not work if the reflux is severe or if you have GERD. Nevertheless, they are readily available over the counter and may help neutralize some of the acid.
According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, there are a few different options for treating GERD, including taking medication, changing your diet and lifestyle, or combining both.
Common medications for treating GERD include (6):
- Antacids: Over-the-counter antacids help neutralize stomach acid. Popular brand names include Rolaids and Tums.
- H2 receptor blockers: These drugs help to cut the amount of stomach acid produced. They are over-the-counter medications and are also available online or by prescription. Popular brand names include Tagamet and Pepcid AC. Zantac has been removed from the US per the Food and Drug Administration as of April 2020 due to cancer concerns.
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs): PPIs block acid production longer than H2 receptor blockers. Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) can relieve GERD symptoms and promote esophageal tissue healing. They are available both on prescription and over-the-counter. Popular brand names include Prevacid, Prilosec, and Nexium.
Surgeries for GERD
GERD can often be managed with medication along with dietary and lifestyle changes. Still, if they are ineffective and you want to avoid long-term medication use, your doctor may recommend surgery.
The most common surgeries for GERD include (7):
- Fundoplication, where the surgeon tightens the lower esophageal sphincter by wrapping the stomach’s top around it to prevent reflux.
- LINX device, where the surgeon wraps a ring of small magnetic beads around the connection point of the stomach and esophagus. These beads possess enough magnetic force to keep the junction sealed and prevent acid reflux yet remain gentle enough to permit food to pass through.
- Transoral incisionless fundoplication (TIF): This new procedure involves using polypropylene fasteners to create a partial wrap around the lower esophagus and tighten the lower esophageal sphincter.
Muscle Tension Dysphonia
If you’re dealing with muscle tension dysphonia, the main form of treatment is voice therapy with a speech-language pathologist. This therapy is designed to alleviate throat tension and improve the overall efficiency of your vocal cords.
You may also be advised to pursue other treatments, such as acupuncture and massage, to help release overall bodily tension. Psychotherapy may also be helpful in soothing muscle tension.
Allergic Reactions
If you experience a life-threatening allergic reaction, administering epinephrine is critical. If you don’t have epinephrine, call 911 or go to a hospital immediately to receive this vital medication.
Once you arrive in the ER, you will be administered epinephrine and other treatments, such as antihistamines. It’s important never to delay emergency medical care if you suspect that you’re having a severe allergic reaction.
Anxiety
Typical treatment options for anxiety include psychotherapy and medication. If you have an anxiety disorder, the best treatment is a combination of cognitive behavior therapy and medication.
Additionally, relaxation techniques, such as progressive muscle relaxation, are helpful for soothing anxiety. Meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises are also great for mind and body relaxation.
Goiter
The approach for treating thyroid goiter depends on its underlying cause. If the reason is an insufficient iodine intake, supplements could be helpful. In some instances, thyroid hormone therapy could be required. Surgical intervention may become necessary if medication fails to reduce the goiter’s size.
Throat Infections
The treatment for throat infections depends on the underlying cause. Antibiotics may be prescribed in the case of a bacterial infection, like strep throat and bacterial tonsillitis.
For viral throat infections, your healthcare provider will likely work with you on a treatment plan that may include acetaminophen for pain and fever, lozenges to soothe a sore throat and bed rest. It usually clears up on its own within one week.
If you have a sore throat, gargling with warm salt water several times daily should reduce infection and ease pain. Drinking honey and lemon tea may also help with the pain and throat inflammation.
Summary
Several conditions can lead to a tightness in your throat, such as GERD, an allergic reaction, strep throat, anxiety, and throat disorders like esophageal stricture.
It is important to consult a medical professional if you experience persistent throat tightness. This can help determine the cause and find the best treatment to improve your quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
How do I get rid of the tightness in my throat?
If your condition is caused by a viral infection, you can alleviate symptoms by getting some rest, drinking warm liquids, using throat lozenges, and gargling with saltwater to soothe throat pain and tightness. You can also take ibuprofen or acetaminophen to alleviate fever and pain. However, if your condition is caused by a bacterial infection, antibiotics prescribed by your doctor may be necessary.
If throat tightness is caused by GERD, over-the-counter or prescription antacids may help neutralize the acids. Your doctor may recommend other medications that reduce stomach acid production. They may also suggest specific dietary and lifestyle changes.
If a tight throat is a symptom of a severe allergic reaction, call 911 or go to the emergency room immediately.
Why does my throat feel tight, but I’m not sick?
You normally will not feel sick with tightness in the throat unless it’s caused by a bacterial or viral throat infection. The most common causes of throat tightness are GERD, anxiety, allergic reaction, goiter, throat infections like strep throat, and muscle tension dysphonia,
Is throat tightness serious?
Feeling tightness in the throat could be a serious emergency, especially for those with allergies. It might be a sign of anaphylaxis, which requires immediate medical attention. It is crucial to seek emergency treatment right away, particularly after exposure to an allergen, to prevent symptoms from worsening.
Why does my esophagus feel tight?
If you’re experiencing tightness in your throat, it could be due to an esophageal stricture. Although other conditions like strep throat, sinus infections, or allergic reactions can also cause throat tightness, an esophageal stricture is typically caused by chemicals like stomach acid burning the esophagus. GERD and acid reflux diseases are the most prevalent causes of esophageal strictures.

- New Report Says Your Brain Could Be the Key to Reducing Phlegm Over 50
- Doctor's "Leave The Throat Phlegm Behind" Tutorial Goes Viral With People Over 50
- Can You Relieve Throat Phlegm and Coughing In 60 Seconds A Day? This Doctor Says Yes
- How To Banish Phlegm When 50+ (Do This Every Day)
References
1- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441938/
2- https://www.jnmjournal.org/journal/view.html?doi=10.5056/jnm18140
3- https://www.jaci-inpractice.org/article/S2213-2198(20)31012-6/fulltext
4- https://aafa.org/allergies/allergy-facts/
5- https://www.thyroid.org/goiter/
6- https://www.jacionline.org/article/S0091-6749(20)30105-6/fulltext
7- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/gerd/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20361959
Dr. Matthew Olesiak continues to make a significant impact in the medical field through his work at SANESolution and his dedication to evidence-based practices.



