What Are Strep Throat Symptoms? All Your Questions Answered!
Are you experiencing strep throat symptoms? Strep throat is an extremely contagious bacterial infection that features an excruciatingly painful sore throat. This condition is caused by group A streptococcus bacteria. Children ages 5 to 15 are most at risk of strep, but adults can also become infected. Cases of strep throat are more prevalent in the spring and winter months.
In this Throat Cleaner and throat diseases blog post, we will take a deep dive into strep throat, exploring its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment. We even provide some ways to prevent strep throat. If you are interested in the world of more throat diseases then you need to make sure to check out our Scarlet Fever and Dysphagia exercises guides!
- Strep throat is caused by the group A Streptococcus pyogenes bacteria.
- A full course of antibiotics is the standard treatment for strep. However, home remedies such as warm salt water gargle, sipping warm liquids, and using a humidifier can help relieve sore throats.
- See your doctor if you suspect you have strep throat, as early antibiotic treatment is essential to a speedy recovery.
How common is strep throat?
The CDC reports that an estimated “several million cases of non-invasive group A strep illnesses occur each year.” (1) Non-invasive strep infections include strep throat, scarlet fever, and impetigo.
The CDC does not track cases of strep throat and other non-invasive infections because symptoms are not as severe as those of the invasive type, and serious complications are rare. Still, strep throat accounts for 15% to 35% of new cases of sore throat (pharyngitis) in children in the United States (2).
What are strep throat symptoms?
The symptoms of strep throat can include:
- The sudden onset of a sore throat
- Pain when swallowing
- Small red spots on the roof of the mouth, toward the throat area
- Red, swollen tonsils
- Pus or white patches on the tonsils
- Swollen glands (lymph nodes) on the neck
- Fever
- Skin rash
- Headache
- Muscle aches
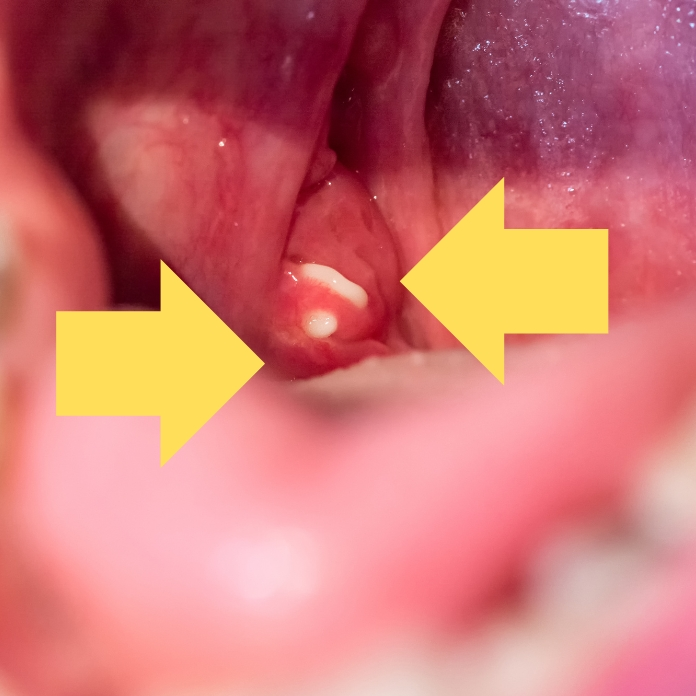
How do I know if my sore throat is strep?
Unlike most sore throats, strep often includes reddened, swollen tonsils. There can also be white streaks of pus on the tonsils.
Is strep throat contagious?
Yes. Strep throat is a highly contagious infection that can be spread even by those who don’t show symptoms or appear unwell. It’s important to note that those exhibiting symptoms or appearing sick are more likely to spread the infection to others.
How do I get strep throat?
Strep throat-causing bacteria can quickly spread through an infected person’s oral and nasal secretions and droplets. When an infected person sneezes, coughs, talks, etc., these droplets can be released into the air, potentially infecting others. The bacteria can survive in small amounts of an infected person’s saliva or nasal discharge.
How long is a person contagious with strep throat?
People with strep throat taking antibiotic treatment become less contagious within 24-48 hours, as opposed to untreated individuals who can infect others for up to three weeks.

How long should you quarantine with strep throat?
If you are experiencing symptoms of strep throat, it is essential to know that you are contagious and should avoid going to work or school. After beginning antibiotic treatment, it is recommended to continue staying home until you have been taking the medication for at least 24 hours.
How do I know if my sore throat is viral or bacterial?
Determining whether your sore throat is viral or bacterial typically depends on the symptoms you experience. Viral sore throats are commonly associated with cough, throat swelling, and runny nose, whereas bacterial sore throats often come with nausea, vomiting, and stomach ache. Symptoms of bacterial throat infections also do not include cough.
With strep, sore throat occurs suddenly. Other strep throat symptoms may include high fever, headache, swollen glands, swollen tonsils, and pain when swallowing.
Can I have strep throat without a sore throat?
Yes. Those found to have strep bacteria in the back of their throats but do not exhibit a sore throat or other symptoms are called “carriers” of the disease. As they are unlikely to become ill, suffer complications, or spread strep throat to others, they typically do not have to take antibiotics (3).
How serious is strep throat?
Most people recover completely from strep throat when taking antibiotics as directed. However, complications can occur, especially with untreated strep throat, including:
- Rheumatic fever. This is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system mistakenly attacks the joints, heart, skin, and/or brain, causing them to swell. Rheumatic fever can cause permanent heart damage.
- Post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis or PSGN. This is a condition characterized by kidney inflammation. Like rheumatic fever, PSGN is an autoimmune disorder that causes the immune system to attack the kidneys.
- Sinus infection (Sinusitis)
- Ear infection
- Scarlet fever. This condition is characterized by a bright red skin rash all over the body.

How is strep throat diagnosed?
When diagnosing strep throat, a doctor will typically use one of two tests: a rapid strep test or a throat culture. In both cases, the doctor will use a cotton-tipped swab to collect a sample from the patient’s throat to diagnose strep throat.
A rapid strep test can provide quick results but may not be as accurate as a throat culture. The throat culture test is designed to determine if strep bacteria are present in the sample collected from the swab.
If a patient shows signs of strep throat but receives a negative result from a rapid strep test, their doctor may recommend a throat culture to ensure the infection was not missed during the initial examination.
What is the treatment for strep throat?
The most common treatment for strep throat is antibiotics. When you take antibiotics for strep throat, you will likely notice an improvement in symptoms within a day or two.
However, it’s essential to take all of the medication to ensure the infection is entirely controlled and to reduce the possibility of complications. Following the prescription as directed will also help alleviate discomfort and prevent the spread of the disease.
Can strep go away without antibiotics?
Yes. Strep throat typically resolves itself without treatment within about one week. However, you can remain contagious for up to three weeks. For this reason, and to reduce the risk of complications, a full course of antibiotics is recommended immediately upon diagnosis.

Are there any natural ways to treat strep throat?
There are no natural ways to kill the streptococcus bacteria that causes strep throat. However, several natural remedies have been shown to help relieve the sore throat of strep, including:
- Gargling with warm salt water
- Drinking warm liquids, like bone broth
- Eating soft foods
- Sucking on ice chips
- Drinking elderberry tea or taking elderberry capsules
- Taking vitamin C, which helps fight infectious diseases like strep
- Use a humidifier to relieve dry and painful throat
How long does strep throat last?
Strep throat typically lasts for a period of three to five days. It is crucial to note that taking antibiotics is highly recommended to minimize the spread of the infection, alleviate symptoms, and prevent further complications.
After 24 hours of antibiotic treatment and no signs of fever, individuals with strep throat can safely return to work, school, or daycare without the risk of infecting others.
What are the risk factors for strep throat?
Several factors can make strep infection more likely, including:
- Age. Children 5-15 are more likely to contract strep throat (4)
- Season. This disease spreads more often in the spring and winter seasons.
- Group settings. Those in large group settings — such as schools and daycare centers — are at significantly increased risk of becoming infected with strep bacteria.

How do I prevent strep infection?
To avoid getting strep throat, you can take a few precautions. By adopting the healthy habits below, you can successfully protect yourself and those around you from acquiring a new or recurring infection.
- Wash your hands. The CDC recommends washing your hands for at least 20 seconds with soapy, warm water after touching surfaces like doorknobs and light switches in public places, shaking hands, and coughing or sneezing. You must also always wash your hands after using the restroom (5).
- Use alcohol-based hand sanitizer. If soap and water aren’t available, opt for a hand sanitizer that contains at least 60% alcohol to get rid of germs on your hands. Although hand sanitizers do not eliminate all types of germs, they are still effective in removing a significant amount.
- Cover your mouth. To maintain good hygiene, you must cover your nose and mouth with a tissue when you need to sneeze, cough, or blow your nose. Doing this can help prevent the spread of respiratory droplets, which can stay in the air for a while. If you don’t have a tissue, coughing or sneezing into your elbow is recommended (5).
- Quarantine yourself. Stay home from work or school until your fever passes or until 24 hours after taking antibiotics to prevent the spread of strep throat, which is highly contagious.
- Rest. Getting enough sleep is crucial for bolstering your immune system and preventing illness. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends adults have at least seven hours of sleep within 24 hours to stay healthy.
If you’re experiencing strep throat symptoms, seeking medical attention as soon as possible is essential. This condition can be uncomfortable, with symptoms like fever, inflammation, and severe sore throat.
Home remedies won’t be effective in treating strep throat, as they require antibiotics to address the underlying bacterial infection adequately. Failing to get proper treatment can lead to complications and prolonged discomfort.
It’s strongly recommended to consult a healthcare professional who will prescribe antibiotics so that you can start feeling better fast. With proper care, strep throat can be resolved within ten days.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I get rid of strep throat fast?
Taking antibiotics within 48 hours of the onset of illness can decrease the length and severity of symptoms, lower the risk of complications, and prevent the infection from spreading to others. You should start feeling better with proper treatment within a day or two.
Why is strep throat so painful?
When you have strep throat, inflammation occurs in the tonsils and the surrounding area of the throat, resulting in pharyngitis or a sore throat.
How long does the worst part of strep throat last?
Patients with strep throat may experience a worsening of symptoms for 2-3 days before feeling better. While the condition usually resolves on its own within 7-10 days, taking antibiotics can provide relief of symptoms more quickly, typically between the third and fourth day.
Do you cough with strep?
No. Cough and other symptoms, such as runny nose, suggest a viral infection.
What should I eat if I have strep throat?
If you have strep throat, you should consume soft, soothing foods like soups, mashed potatoes, and yogurt. Very cold foods like ice cream also provide relief.
How long should I stay out of work with strep throat?
According to the CDC, individuals with strep throat should stay at home until they have been fever-free for 24 hours and have been taking antibiotics for at least one day. If left untreated, they can continue to spread the infection until they recover.

- New Report Says Your Brain Could Be the Key to Reducing Phlegm Over 50
- Doctor's "Leave The Throat Phlegm Behind" Tutorial Goes Viral With People Over 50
- Can You Relieve Throat Phlegm and Coughing In 60 Seconds A Day? This Doctor Says Yes
- How To Banish Phlegm When 50+ (Do This Every Day)
2- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/4602-strep-throat
3- https://www.cdc.gov/groupastrep/diseases-public/strep-throat.html
4- https://www.cdc.gov/groupastrep/diseases-public/strep-throat.html
5- https://www.cdc.gov/handwashing/when-how-handwashing.html


